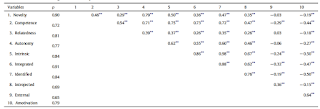
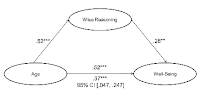
Relationship between mindset, basic psychological needs and well-being

The mindset theory and the self-determination theory are two important pillars of progress-focused work. Within the progress-focused approach, we see both theories as important and complementary frameworks for understanding commitment, progress, and well-being. A new study also looks at the relationships between these two theories, in particular the interplay between mindset and basic psychological needs.